Innovations in Coffee Processing: What West Africa Can Learn and Adopt
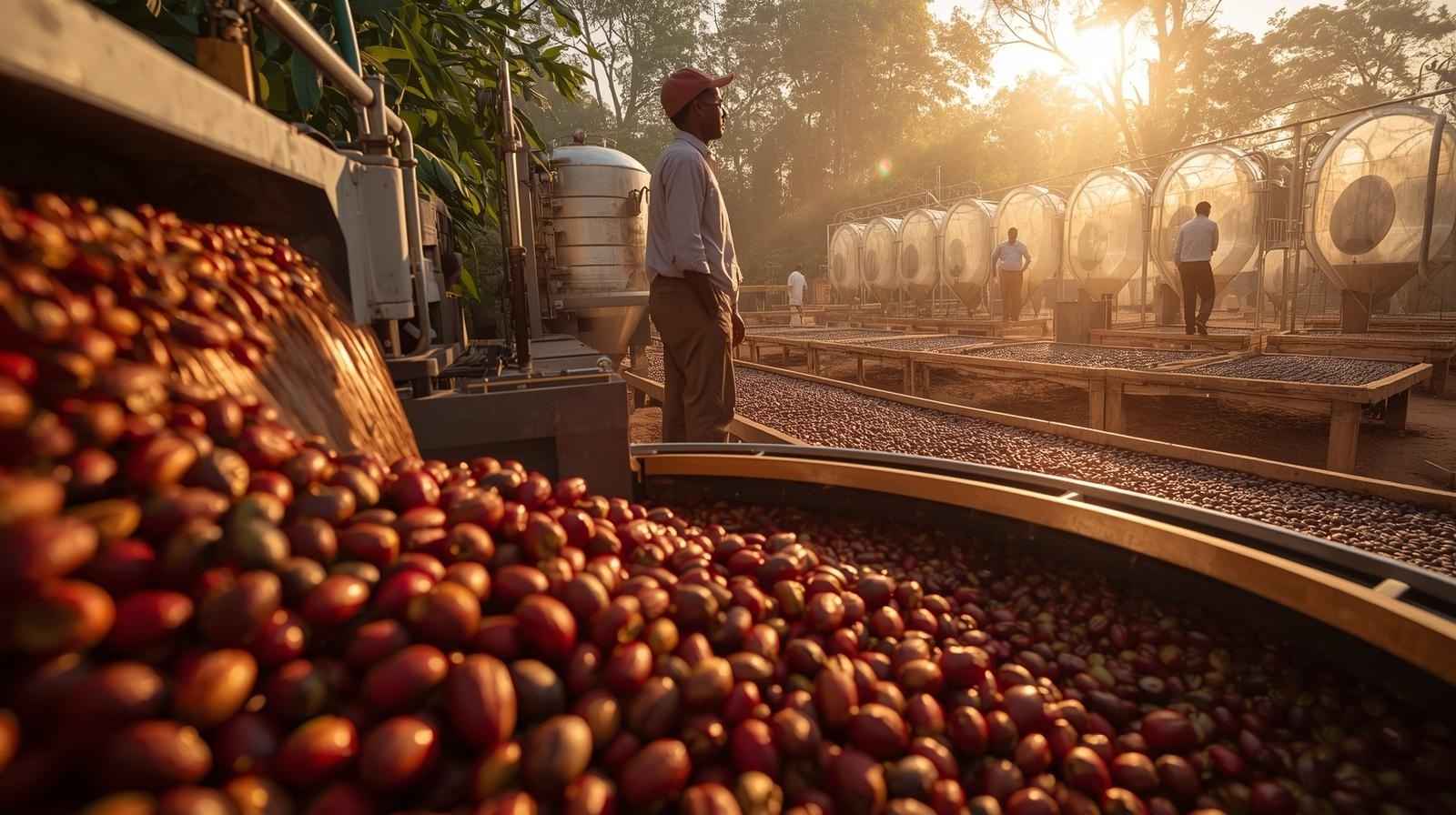
Coffee is more than just a drink — it is a global industry shaped by tradition, technology, and innovation. In recent years, new coffee processing methods have emerged, transforming the quality, flavor, and sustainability of coffee worldwide. For West Africa, where coffee farming holds enormous potential, adopting these innovations can strengthen competitiveness, improve farmer incomes, and showcase the region’s unique coffee identity on the global stage.
In this article, we explore key innovations in coffee processing and what West Africa can learn and adopt to build a thriving coffee industry.
1. Honey Processing
Traditionally, most West African farmers use washed or natural methods. However, honey processing — where part of the mucilage (sticky fruit layer) is left on the bean during drying — is gaining popularity globally. This method enhances sweetness and body while saving water.
Why West Africa Should Adopt It:
- Produces distinctive flavor notes that appeal to the specialty coffee market.
- Reduces water usage compared to fully washed processing.
- Adds value for farmers by creating premium coffee profiles.
2. Anaerobic Fermentation
This cutting-edge method involves fermenting coffee beans in sealed tanks without oxygen. The controlled environment allows for unique flavor development, often producing fruity and exotic taste profiles.
Benefits for West Africa:
- Differentiates West African coffee in international markets.
- Provides opportunities for experimentation and storytelling, boosting market value.
- Encourages collaboration with global specialty buyers interested in rare processing methods.
3. Eco-Friendly Wet Mills
One major challenge in coffee processing is water waste and pollution. New eco-pulpers and eco-friendly wet mills reduce water use by up to 90% while improving efficiency.
How This Helps West Africa:
- Makes processing more sustainable and environmentally responsible.
- Reduces costs for farmers while maintaining coffee quality.
- Aligns with global demand for ethically and sustainably produced coffee.
4. Solar-Powered Drying Systems
Post-harvest drying is critical for coffee quality, but unpredictable rainfall in West Africa often leads to inconsistencies. Solar dryers offer a clean, affordable solution.
Advantages for Farmers:
- Provides consistent, controlled drying conditions.
- Reduces the risk of mold or defects.
- Cuts costs compared to mechanical dryers while promoting renewable energy use.
5. Blockchain and Digital Traceability
Consumers and buyers increasingly want to know where their coffee comes from. Blockchain-based traceability tools allow farmers and cooperatives to document their supply chain digitally, building transparency and trust.
Opportunities for West Africa:
- Boosts credibility of West African coffee in global markets.
- Enables farmers to tell their unique story “from farm to cup.”
- Helps meet certification and export requirements with ease.
Conclusion
The future of West Africa’s coffee industry depends on innovation, sustainability, and quality. By adopting methods such as honey processing, anaerobic fermentation, eco-friendly wet mills, solar-powered drying, and blockchain traceability, farmers and cooperatives can increase competitiveness while reducing environmental impact.
At WASCA (West Africa Specialty Coffee Association), we are committed to empowering farmers with training, knowledge, and access to these innovations. Together, we can position West African coffee as a strong, recognizable force in the global specialty coffee market.